By – James M. Katz, BA
Holistic nursing practice is transforming modern healthcare by embracing a comprehensive approach to patient care. This innovative method considers the whole person – body, mind, and spirit – rather than just treating specific symptoms or illnesses. Holistic nurses integrate conventional medical treatments with complementary and alternative therapies to promote healing and wellness. They focus on creating a healing environment that supports the patient’s overall well-being and encourages active participation in the recovery process.
The American Holistic Nurses Association has been instrumental in defining and promoting holistic nursing care. This approach involves a thorough holistic assessment of patients, taking into account their physical, emotional, and spiritual needs. Holistic nurse practitioners use integrative therapies alongside traditional medical interventions to provide patient-centered care. By adopting a holistic approach in nursing, healthcare professionals can address the root causes of health issues and foster long-term wellness. This article will explore the philosophical foundations of holistic nursing, its practical applications, ethical considerations, and the growing body of research supporting its effectiveness in modern healthcare settings.
Holistic nursing is a special way of caring that looks at the whole person, not just their illness. Nurses who practice holistic nursing believe in the strong connection between the body, mind, and spirit. They also make sure to take care of themselves so they can better care for others. This approach helps people heal better from the time they are born until the end of their lives.
Key Takeaways
- Holistic nursing focuses on healing the whole person, including their body, mind, and spirit.
- Nurses in this field believe that taking care of themselves is important for taking care of others.
- Holistic nursing can be practiced in any healthcare setting and with any patient group.
- This type of nursing has been recognized by the American Nurses Association since 2006.
- Holistic nurses use both science and intuition to provide the best care possible.
Historical Background of Holistic Nursing
Florence Nightingale’s Influence
Florence Nightingale’s work laid the foundation for holistic nursing. She believed in treating the whole person, not just the illness. Her theories emphasized the importance of a healing environment, compassionate care, and the connection between mind, body, and spirit. These ideas continue to shape holistic nursing today.
Evolution Over Time
Holistic nursing has evolved significantly since Nightingale’s time. Initially, it was not widely accepted in mainstream medicine. However, over the years, more healthcare professionals have recognized the value of treating patients holistically. This approach has grown to include various practices that address physical, emotional, and spiritual needs.
Recognition by Professional Bodies
The American Holistic Nurses Association (AHNA) has played a crucial role in promoting holistic nursing. Established in the 1980s, the AHNA has worked to define standards, provide education, and advocate for the recognition of holistic nursing as a specialty. Today, holistic nursing is acknowledged by many professional bodies, reflecting its importance in modern healthcare.
Philosophical Foundations of Holistic Nursing
Holistic nursing is a unique approach to healthcare that focuses on the whole person, not just their physical symptoms. It recognizes the interconnectedness of different aspects of a person’s life rather than just treating their symptoms. This practice emphasizes the importance of the mind-body connection and the role of the environment in maintaining health.
Holism
The concept of holism is at the core of holistic nursing. It involves observing and addressing all dimensions of health, including the mind, spirit, social health, and environment. This approach recognizes that all aspects of a person’s life are interconnected, and addressing one area can also impact others.
Holistic nursing is defined as “all nursing practice that has healing the whole person as its goal”. This philosophy can be traced back to Florence Nightingale, who is considered the founder of holistic nursing. Nightingale taught nurses to focus on the principles of holism: unity, wellness, and the interrelationship of human beings and their environment.
Interconnectedness
Holistic nursing is not merely a set of practices but also an attitude, a philosophy, and a way of being. It requires nurses to integrate self-care, self-responsibility, spirituality, and reflection in their lives. This often leads to a greater awareness of the interconnectedness of self, others, nature, spirit, and relationship with the global community.
The holistic approach looks at the big picture, considering overarching patterns, stressors, and habits that can impact a person’s health. Rather than treating problems as if they exist independently, holistic nurses take their patient’s physiology, mental health, spiritual beliefs, and social environment into account, caring for the entirety of the human being.
Healing vs. Curing
A fundamental aspect of holistic nursing philosophy is the distinction between healing and curing. Curing means to eliminate sickness, while healing refers to repairing the body, mind, or spirit. Healing involves a journey that provides intelligence from experience and may involve change and acceptance of that change.
Holistic nurses understand that healing can come in many forms other than cure. When a clinician helps ease a patient’s mind with accurate information, realistic expectations, and a humane touch, healing can still take place even if a cure is not possible. This approach is particularly important when dealing with chronic or incurable conditions.
The holistic nursing philosophy emphasizes the concept of intrinsic hope, which centers on the present day and brings inner peace to a patient’s life. This replaces unrealistic expectations for recovery with a more profound and resilient emotional foundation. By focusing on healing rather than just curing, holistic nurses can provide compassionate care that addresses the spiritual and emotional aspects of health, contributing to a more comprehensive and patient-centered approach to healthcare.
Core Principles of Holistic Nursing
Integration of Self-Care
Holistic nursing believes that nurses need to take care of themselves to help others better. When nurses practice self-care, they can be more aware and healthy, making them better healers. This principle is about making sure nurses are in good shape, both in body and mind, so they can give the best care to their patients.
Mind-Body-Spirit Connection
Holistic nursing sees health as a mix of the mind, body, and spirit. This means that to help someone get better, nurses look at all parts of a person, not just the physical symptoms. By understanding this connection, nurses can provide care that helps the whole person, not just one part.
Holistic Ethics and Values
Holistic nursing is guided by strong ethics and values. Nurses follow these principles to make sure they are doing the right thing for their patients. This includes being honest, fair, and respectful. By sticking to these values, nurses can build trust and provide better care.
The Holistic Nursing Process
The holistic nursing process is a comprehensive approach to patient care that considers the whole person – body, mind, and spirit. This process consists of five interconnected steps that guide nurses in providing holistic care.
Assessment
The first step in the holistic nursing process is assessment. This involves a thorough and holistic evaluation of the patient, including both subjective and objective data collection. Holistic assessment goes beyond traditional methods by considering various aspects that may impact a person’s health, such as physical, mental, social, financial, and environmental factors.
During this stage, nurses gather information about the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and overall functioning. They may conduct physical exams, psychological assessments, and other diagnostic tests. The assessment also includes evaluating the patient’s social support network, living conditions, and access to resources and services.
Diagnosis
Based on the data collected during the assessment, nurses form a nursing diagnosis. This diagnosis directs nursing-specific patient care and must be approved by NANDA International (NANDA-I) . In holistic nursing, the diagnosis considers not only physical symptoms but also psychological, emotional, social, and spiritual aspects of the patient’s well-being.
Psychosocial nursing diagnoses are particularly important in holistic care, as they address psychological, emotional, social, and spiritual aspects of nursing care. These diagnoses can include issues related to self-esteem, body image, hopelessness, caregiver role strain, and grieving.
Planning
The planning phase involves developing a patient care plan based on the nursing diagnosis. This plan should be measurable and goal-oriented, focusing on the patient and their family members. In holistic nursing, the planning process is collaborative, with nurses and patients working together to establish wellness goals.
Holistic care plans consider the unique challenges, strengths, and goals of each patient. They may include a variety of approaches, such as medication, education, communication, self-help, and complementary treatments.
Implementation
Implementation is the phase where nurses put the care plan into action. This step provides continuous care during hospitalization until discharge. In holistic nursing, implementation involves a wide range of approaches that address the patient’s physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual needs.
Holistic nurses use various techniques to deliver care, including:
1. Compassionate and attentive presence
2. Comprehensive treatment addressing mind, body, and spirit
3. Curiosity about factors affecting health, such as environmental influences and dietary choices
Evaluation
The final step in the holistic nursing process is evaluation. During this phase, nurses assess the effectiveness of the care plan based on specific goals and desired outcomes. They may adjust the plan as needed to better meet the patient’s needs.
Evaluation in holistic nursing considers not only physical improvements but also changes in the patient’s overall well-being, including their mental, emotional, and spiritual state. This comprehensive evaluation helps ensure that the care provided truly addresses the whole person.
By following this holistic nursing process, nurses can provide more comprehensive and personalized care that addresses all aspects of a patient’s health and well-being. This approach can lead to improved patient outcomes, increased patient satisfaction, and a more fulfilling practice for nurses themselves.
Holistic Nursing in Clinical Practice
Application in Various Settings
Holistic nursing is practiced in many places, like hospitals, schools, and private clinics. Nurses use holistic methods to help people heal and grow. They focus on the whole person, not just the illness.
Therapeutic Relationships
Building strong, caring relationships with patients is key in holistic nursing. Nurses listen and support patients, making them feel safe and understood. This helps in the healing process.
Holistic Modalities
Holistic nurses use different methods to care for patients. These can include things like meditation, massage, and energy healing. They aim to treat the mind, body, and spirit together.
Integrating Holistic Principles in Conventional Healthcare
The integration of holistic principles into conventional healthcare is transforming patient care, offering a more comprehensive and patient-centered approach. This integration addresses the growing demand for evidence-based care that considers the whole person – body, mind, and spirit . By combining the strengths of both holistic and conventional medicine, healthcare providers can enhance outcomes for patients dealing with complex health issues.
Collaborative Practice
Collaborative care models have been introduced in various parts of the world, particularly in countries with strong primary care sectors, to address the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases. This approach recognizes the need for collaboration between health and social care to support patients effectively. Integrating functional medicine with conventional practices creates a comprehensive approach to patient care, focusing on identifying root causes of illnesses while providing evidence-based treatments.
To foster successful collaboration, healthcare providers can implement several strategies:
1. Joint clinical rounds: These provide opportunities for practitioners from different fields to discuss patient cases and offer diverse insights.
2. Shared patient case studies: This practice allows functional and conventional practitioners to learn from each other’s experiences and treatment outcomes.
3. Collaborative treatment protocols: Designing treatment plans together facilitates the creation of holistic care plans and fosters mutual understanding among diverse teams of clinicians, administrative staff, patients, and their families.
Patient-Centered Care
Holistic care is at the heart of nursing science and has important consequences in healthcare systems. It addresses patients’ physical, emotional, social, and spiritual needs, helping to restore balance and enabling them to cope with their illnesses. This approach considers the patient as a whole within their environment, acknowledging the interdependence of biological, social, psychological, and spiritual aspects.
Key aspects of patient-centered holistic care include:
1. Empowering patients: Restoring power and responsibility to patients and encouraging self-care leads to therapeutic consultation, hope, dignity, and personal growth.
2. Equality in relationships: The relationship between holistic care providers and patients is based on relative openness, equality, and mutuality.
3. Cultural and spiritual considerations: Holistic care takes into account patients’ culture and spiritual well-being.
The benefits of this approach are significant. Holistic care has been shown to prevent depression in patients, improve physical conditions, decrease the duration of hospitalization, and promote faster recovery.
Cultural Competence
Cultural competence in healthcare is crucial for addressing disparities experienced by people from diverse racial and cultural backgrounds. It involves delivering effective, quality care to patients with diverse beliefs, attitudes, values, and backgrounds. Cultural competence aims to break down barriers that hinder patients from receiving the care they need and ensures improved understanding between patients and their providers.
Implementing cultural competence in healthcare can lead to several benefits:
1. Increased patient safety and reduced inefficiencies
2. Reduced care disparities and decreased costs
3. Improved patient outcomes and experiences
To promote cultural competence, healthcare organizations can:
1. Provide cultural competence training to healthcare providers
2. Collect and analyze demographic data to better understand local communities
3. Recruit and retain team members who reflect the populations they serve
By integrating holistic principles, fostering collaborative practices, focusing on patient-centered care, and promoting cultural competence, healthcare providers can offer a more nuanced and effective care model that better meets patient demands for a healthcare system that values and addresses all aspects of their health.
Challenges and Opportunities in Holistic Nursing
Barriers to Implementation
Holistic nursing faces several hurdles in its implementation. One major challenge is the lack of understanding and acceptance among healthcare professionals. Many still view holistic practices as unscientific or secondary to traditional medical treatments. Additionally, there are often limited resources and support for holistic approaches within healthcare institutions. This can make it difficult for nurses to fully integrate holistic methods into their practice.
Opportunities for Growth
Despite these challenges, there are numerous opportunities for growth in holistic nursing. As more research supports the benefits of holistic care, acceptance is gradually increasing. Nurses have the chance to lead the way in integrating holistic practices into mainstream healthcare. This can improve patient outcomes and satisfaction. Furthermore, there are growing educational programs and certifications that help nurses specialize in holistic care, providing them with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in this field.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, the future of holistic nursing appears promising. There is a growing emphasis on patient-centered care, which aligns well with holistic principles. Advances in technology and research are also opening new doors for holistic practices. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, holistic nursing is likely to become more widely recognized and valued. This will create more opportunities for nurses to make a meaningful impact on their patients’ lives through holistic care.
Holistic Nursing and Patient Outcomes
Impact on Patient Satisfaction
Holistic nursing has a significant impact on patient satisfaction. By addressing the mind, body, and spirit, holistic nurses create a more personalized and compassionate care experience. Patients often feel more understood and valued, leading to higher satisfaction levels.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies highlight the benefits of holistic nursing. For example, patients receiving holistic care often report improved emotional well-being and faster recovery times. These real-life examples demonstrate the effectiveness of a holistic approach in various healthcare settings.
Research Findings
Research supports the positive outcomes associated with holistic nursing. Studies show that holistic practices can lead to better patient outcomes, including reduced stress and improved overall health. This evidence underscores the importance of integrating holistic methods into standard nursing practice.
Self-Care Strategies for Holistic Nurses
Mindfulness Practices
Holistic nurses often use mindfulness practices to stay present and focused. These practices help them manage stress and maintain a calm demeanor, which is essential for providing quality care. Mindfulness can also improve emotional resilience, allowing nurses to better handle the challenges of their profession.
Physical Wellness
Maintaining physical wellness is crucial for holistic nurses. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep are fundamental components. By taking care of their bodies, nurses ensure they have the energy and stamina needed for their demanding roles. Physical wellness also contributes to overall mental and emotional health.
Emotional Resilience
Emotional resilience is the ability to bounce back from stressful situations. Holistic nurses build this resilience through various self-care practices, such as journaling, meditation, and seeking support from colleagues. Developing emotional resilience helps nurses stay compassionate and effective in their caregiving roles.
Holistic Self-Care for Nurses
Holistic self-care is crucial for nurses to maintain their well-being and provide quality care to patients. This approach considers the whole person – body, mind, and spirit – and emphasizes the importance of self-awareness and self-responsibility. Nurses who value themselves and mobilize necessary resources for self-care are better equipped to handle the challenges of their profession.
Stress Management
Stress management is a critical aspect of holistic self-care for nurses. The demanding nature of nursing can lead to high levels of stress, which, if left unchecked, can result in burnout, acute stress disorder, secondary traumatic stress, and even post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
To combat stress, nurses can employ various strategies:
1. Practice mindfulness and meditation: Regular mindfulness practices can help shrink the amygdala, the brain’s center for fight or flight responses, leading to more relaxed and mindful reactions.
2. Engage in progressive muscle relaxation (PMR): PMR reduces cortisol and adrenalin levels, decreases heart rate and oxygen consumption, and relaxes skeletal muscle activity.
3. Try diaphragmatic breathing: This technique originates in the belly and can help release stress through slow, full breaths.
4. Explore energy therapies: Practices like Jin Shin Jyutsu Self-Help have been shown to decrease stress and improve emotional vitality.
5. Use guided imagery: This non-invasive technique can induce relaxation and encourage the healing process.
Work-Life Balance
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is essential for nurses to prevent burnout and ensure job satisfaction. Nurses who regularly sacrifice their personal lives for work often experience emotional exhaustion and decreased job performance.
To achieve a better work-life balance:
1. Set clear goals: Identify short-term and long-term goals for both professional and personal life.
2. Prioritize tasks: List tasks from most important to least important and learn to say no when necessary.
3. Schedule self-care: Use time blocking to schedule not only work obligations but also rest, relaxation, and hobbies.
4. Take advantage of paid time off: Using PTO opportunities is an important aspect of self-care.
5. Seek support: Regularly receiving emotional support from friends, family, and colleagues can help nurses better handle work challenges.
Personal Growth
Personal growth is an integral part of holistic self-care for nurses. It involves continuous learning, self-reflection, and the development of coping strategies. To foster personal growth:
1. Engage in lifelong learning: Pursue ongoing education and self-assessment to develop authentic and deep introspection.
2. Practice self-reflection: Use journaling to record thoughts, feelings, and insights, which can help reduce anxiety and stress.
3. Develop resilience: Regular mindful practice can cultivate resilience, helping nurses to “ground” themselves and make thoughtful decisions under stressful circumstances.
4. Nurture spirituality: Incorporating spiritual practices like prayer can contribute to emotional catharsis and help cope with the pressures of tragic or painful situations.
5. Embrace physical activity: Regular exercise, such as yoga or meditative walking, can help release bodily tensions, clear the mind, and restore inner peace [43, 44].
By incorporating these holistic self-care practices into their daily routines, nurses can better manage stress, achieve a healthier work-life balance, and foster personal growth. This comprehensive approach to self-care enables nurses to maintain their own well-being while providing compassionate and effective care to their patients.
Holistic Approaches to Common Health Issues
Holistic approaches to healthcare consider the whole person – body, mind, and spirit – rather than just treating specific symptoms or illnesses. These approaches have gained popularity in addressing various common health issues, offering complementary or alternative methods to conventional treatments.
Chronic Pain
Chronic pain affects millions of people worldwide, and holistic approaches have shown promise in managing this condition. A growing body of evidence suggests that complementary therapies can help alleviate pain and improve quality of life.
Some effective holistic approaches for chronic pain include:
1. Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese practice has been found to be more effective than no treatment or sham acupuncture for back or neck pain.
2. Mindfulness-based interventions: Studies have shown that mindfulness-based stress reduction can lead to small improvements in chronic low-back pain.
3. Yoga and Tai Chi: These mind-body practices have demonstrated benefits for various types of chronic pain, including low-back pain and osteoarthritis.
4. Massage therapy: While the evidence is weak, some studies suggest that massage may be helpful for low-back pain.
5. Herbal remedies: Topical products containing cayenne have shown evidence of reducing pain, while other herbs like comfrey and lavender essential oil may also be beneficial.
Mental Health
Holistic approaches to mental health focus on treating the whole person, addressing not only psychological symptoms but also physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects of well-being.
Some effective holistic strategies for mental health include:
1. Mindfulness and meditation: These practices can help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression symptoms in people with chronic pain.
2. Recreational therapy: Activities such as arts and crafts, sports, and community outings can help lower stress and anxiety while building confidence and improving communication.
3. Equine therapy: Working with horses has been shown to develop self-esteem, address fear and anxiety, and promote empathy in individuals with substance use and mental health disorders.
4. Creative expression: Art therapy, music therapy, and other forms of self-expression have been proven effective in promoting positive emotion regulation and self-development.
5. Yoga and physical activity: These practices can improve mental calmness, flexibility, and overall well-being.
Cardiovascular Disease
Holistic approaches can play a significant role in preventing and managing cardiovascular disease.
Some effective strategies include:
1. Physical activity: Regular, moderate to vigorous-intensity activity for at least 30 minutes, five days a week, can help ward off risk factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels.
2. Healthy diet: A heart-healthy eating plan that includes colorful fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help protect the heart and improve blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
3. Stress management: Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease risk factors. Holistic approaches such as mindfulness, yoga, and meditation can help manage stress effectively.
4. Sleep hygiene: Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for heart health. Adults who get less than 7 hours of sleep per night are more likely to have health problems, including high blood pressure.
5. Holistic lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking, moderating alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight are all important factors in preventing cardiovascular disease.
By incorporating these holistic approaches, individuals can address common health issues more comprehensively, potentially improving their overall well-being and quality of life.
Research and Evidence in Holistic Nursing
Current Studies
The field of holistic nursing is experiencing a surge in research activity, with numerous studies exploring various aspects of holistic care and its impact on patient outcomes. Recent research has focused on the effectiveness of complementary therapies in managing common health issues. For instance, studies have shown that acupuncture can be more effective than no treatment or sham acupuncture for back or neck pain. Additionally, mindfulness-based stress reduction interventions have demonstrated small improvements in chronic low-back pain.
Current research also explores the impact of holistic nursing practices on specific patient populations. For example, ongoing studies are investigating the effects of Reiki on pain management in cancer patients and its influence on the perception of quality of life after postpartum psychosis. Another study is examining the relationship between yoga practice dosage and perceived stress, anxiety, and self-reported health among breast cancer survivors.
Methodological Challenges
Despite the growing body of research in holistic nursing, researchers face several methodological challenges. One significant obstacle is the difficulty in measuring holistic outcomes, which often involve subjective experiences and complex interactions between physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects of health. This complexity can make it challenging to design studies that capture the full scope of holistic care’s impact.
Another challenge lies in the integration of holistic principles into research designs. The holistic approach emphasizes the interconnectedness of various aspects of a person’s life, which can be difficult to isolate and study using traditional research methods. Researchers must develop innovative approaches that can account for these complex relationships while maintaining scientific rigor.
Furthermore, the lack of standardization in holistic nursing practices can make it difficult to compare results across studies. Different practitioners may employ varying techniques or approaches, leading to inconsistencies in research outcomes.
Holistic Nursing Across the Lifespan
Pediatric Holistic Care
Holistic nursing for children focuses on nurturing their physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being. Nurses aim to create a comforting environment that supports the child’s overall health and development. This approach helps in building trust and reducing anxiety in young patients.
Adult Holistic Care
In adult care, holistic nursing addresses the diverse needs of individuals by considering their life experiences and personal beliefs. Nurses work to balance physical treatments with emotional and spiritual support, ensuring comprehensive care. This method promotes healing and enhances the patient’s quality of life.
End-of-Life Holistic Care
Holistic nursing at the end of life emphasizes comfort, dignity, and peace. Nurses provide compassionate care that respects the patient’s wishes and supports their family. By focusing on the whole person, this approach helps patients find meaning and closure in their final days.
Future Directions
The future of holistic nursing research holds promising opportunities for advancing the field and improving patient care. One key area of focus is the development of more robust research methodologies that can effectively capture the multidimensional nature of holistic care. This may involve the creation of new assessment tools and outcome measures that better reflect the holistic approach to health and wellness.
Additionally, there is a growing interest in exploring the integration of holistic nursing practices within conventional healthcare settings. Future studies may investigate the impact of holistic care on patient satisfaction, treatment costs, and hospital stay durations. This research could provide valuable evidence to support the wider adoption of holistic nursing practices in mainstream healthcare.
Another important direction for future research is the examination of factors that influence nurses’ ability to practice holistic care. Studies may explore the impact of education, organizational support, and personal beliefs on nurses’ implementation of holistic care principles. This research could inform the development of interventions aimed at enhancing nurses’ practice of holistic care and, ultimately, improving patient outcomes and safety.
As the field of holistic nursing continues to evolve, researchers will need to stay attuned to emerging challenges and opportunities in healthcare. Future studies may address new environmental, personal, health, and nursing issues that arise, ensuring that holistic nursing research remains relevant and responsive to changing healthcare needs.
Ethical Considerations in Holistic Nursing
Holistic nursing practice emphasizes treating the whole person – body, mind, and spirit. This approach brings unique ethical considerations that nurses must navigate to provide compassionate, patient-centered care while maintaining professional boundaries. Three key areas of ethical consideration in holistic nursing are informed consent, cultural sensitivity, and professional boundaries.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is a fundamental ethical principle in healthcare that respects patient autonomy and promotes trust between patients and healthcare providers. In holistic nursing, informed consent involves more than just obtaining a signature on a form. It is an ongoing process of communication and shared decision-making between the nurse and the patient.
The process of informed consent in holistic nursing includes:
1. Providing clear and understandable information about proposed treatments, including their purpose, potential risks, and benefits.
2. Explaining alternative treatment options and their potential outcomes.
3. Ensuring the patient has the capacity to understand the information and make an informed decision.
4. Allowing the patient to ask questions and voice concerns.
5. Respecting the patient’s right to accept or refuse treatment without fear of negative consequences.
Nurses play a crucial role in the informed consent process by ensuring patient comprehension, facilitating documentation, addressing patient anxiety, and identifying appropriate surrogate decision-makers when needed. This collaborative approach between nurses and other healthcare professionals helps to reduce the risk of litigation and meets legal obligations imposed by informed consent statutes.
Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural sensitivity is essential in holistic nursing practice, particularly given the changing demographic landscape https://www.practicalnursing.org/importance-holistic-nursing-care-how-completely-care-patients in the United States. The concept of cultural humility has emerged as a more effective approach than cultural competence in addressing the diverse needs of patients.
Cultural humility emphasizes:
1. Self-reflection and critique of one’s own biases and assumptions.
2. Recognizing patients as experts of their own cultural experiences.
3. Lifelong learning and partnership-building with patients and communities.
4. Valuing each person’s cultural and educational background, including life experiences.
Nurses can practice cultural humility by:
1. Using plain language and vocabulary familiar to patients.
2. Acknowledging that patients are the experts of their experiences and culture.
3. Continuously reflecting on and critiquing their own thoughts, sensations, judgments, and perceptions.
4. Being cognizant of social or cultural influences that may have led to a patient’s current situation.
By embracing cultural humility, nurses can provide more effective, patient-centered care and help address health inequities in diverse populations.
Professional Boundaries
Maintaining professional boundaries is crucial in holistic nursing to protect both patients and nurses. Professional boundaries are defined as “the spaces between the nurse’s power and the patient’s vulnerability” https://ojin.nursingworld.org/table-of-contents/volume-6-2001/number-2-may-2001/holistic-nursing-practice/ . These boundaries help nurses maintain a therapeutic relationship with patients while avoiding potential ethical violations.
Key considerations for maintaining professional boundaries include:
1. Avoiding inappropriate behaviors such as sharing personal information, exchanging gifts, or developing formal relationships with patients.
2. Dressing and acting professionally to reinforce the nurse’s role as a trained healthcare provider.
3. Protecting patient confidentiality by refraining from discussing patient information unnecessarily.
4. Providing patient-centered care that prioritizes the patient’s needs and dignity.
Nurses should be aware of potential boundary violations, such as:
1. Over-sharing personal information or seeking emotional support from patients.
2. Accepting or giving gifts, which can shift expectations about the nurse-patient relationship.
3. Exchanging money or engaging in financial transactions with patients.
4. Any form of sexual or romantic involvement with patients, which is considered sexual misconduct.
To maintain professional boundaries, nurses should regularly reflect on their interactions with patients, seek guidance from colleagues when unsure, and prioritize the patient’s well-being in all decisions and actions.
By carefully considering these ethical aspects of holistic nursing practice, nurses can provide compassionate, patient-centered care while maintaining professional integrity and protecting both themselves and their patients.
Conclusion
Holistic nursing practice has a significant impact on modern healthcare, offering a comprehensive approach to patient care that considers the whole person – body, mind, and spirit. This innovative method integrates conventional medical treatments with complementary therapies to promote healing and wellness. By focusing on creating a healing environment and encouraging patients to take an active role in their recovery, holistic nursing has the potential to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction.
The growing body of research supporting holistic nursing practices highlights its effectiveness in addressing various health issues, from chronic pain management to mental health support. As healthcare continues to evolve, the integration of holistic principles into conventional settings presents both challenges and opportunities. To move forward, it’s crucial to address ethical considerations, maintain professional boundaries, and continue to develop evidence-based practices that honor the holistic approach to healthcare.
If you are a registered nurse and are interested in learning more about Holistic Nursing and Integrative healthcare, we offer an online certification program in holistic healthcare. In order to complete our program you would need to have your RN License and complete our 5 online holistic nursing courses. All of our exams are 100% online, on open enrollment and self-paced. If you want to review our Holistic Nursing Certification program, please click here!
FAQs
- What is holistic nursing?
Holistic nursing is a way of nursing that cares for the whole person. This means looking after the body, mind, and spirit. It’s about helping people heal from birth to the end of life.
- Where can holistic nurses work?
Holistic nurses can work in many places like hospitals, schools, and private clinics. They can help people in almost any healthcare setting.
- What are the main ideas of holistic nursing?
Holistic nursing focuses on self-care, the connection between mind, body, and spirit, and strong values and ethics. Nurses also need to take care of themselves to help others better.
- How did holistic nursing start?
Holistic nursing has roots in the teachings of Florence Nightingale. It has grown over time and was officially recognized by the American Nurses Association in 2006.
- What are some challenges in holistic nursing?
Some challenges include finding time to practice self-care and getting support from other healthcare workers. But there are also many chances to grow and learn in this field.
- How does holistic nursing help patients?
Holistic nursing can make patients feel more satisfied with their care. It looks at all parts of a person’s life, which can lead to better overall health.
- What does a nurse do in holistic health care?
In holistic nursing, professionals focus on providing care that addresses the entire person rather than just specific health issues. This involves assessing the patient’s lifestyle and other factors to enhance their overall health and wellness.
- Why is holistic care significant in health care?
Holistic care is crucial because it treats the whole person, incorporating physical, mental, emotional, social, and spiritual aspects of health. It utilizes a wide range of disciplines, religious beliefs, and cultural practices to promote healing in individuals, communities, and the environment.
- How does a holistic approach impact nursing practice?
Nurses trained in holistic care are adept at helping patients improve their lifestyle choices and address various determinants of health, including personal, economic, social, and environmental factors that affect their well-being.
- What is the importance of holistic nursing in end-of-life care?
Holistic nursing plays a vital role in end-of-life care by addressing not only the physical but also the emotional, social, and spiritual needs of patients. It facilitates discussions about death, last wishes, and the grieving process, making these difficult times more manageable for patients and their families.
Research Articles:
Digitizing nursing: A theoretical and holistic exploration to understand the adoption and use of digital technologies by nurses. Matthew Wynn, Et Al. JAN. Volume79, Issue 10 October 2023 Pages 3737-3747 First published: 02 August 2023
Access link here
A holistic approach to remote patient monitoring, fueled by ChatGPT and Metaverse technology: The future of nursing education. Manik Sharma, Et Al. Nurse Education Today Volume 131, December 2023, 105972
Access link here
Storytelling: Manifesting Integral Interconnectedness in Holistic Nursing Education. Moore AK. Journal of Holistic Nursing. 2023;41(4):403-410.
Access link here
A Holistic Approach to Undesired Content Detection in the Real World. Markov, T., Et Al. (2023). Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 37(12), 15009-15018.
Access link here
 The vagus nerve is a key component of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “rest and digest” state of our body. This is in contrast to the sympathetic nervous system’s “fight or flight” response. As holistic nurses, we often work with patients to activate their parasympathetic system to promote relaxation and healing.
The vagus nerve is a key component of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “rest and digest” state of our body. This is in contrast to the sympathetic nervous system’s “fight or flight” response. As holistic nurses, we often work with patients to activate their parasympathetic system to promote relaxation and healing.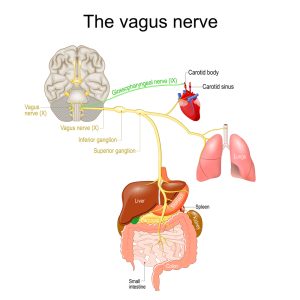










 Written by Veronica Turner
Written by Veronica Turner




























