 Written by Veronica Turner
Written by Veronica Turner
Approximately 17.5% of adults, or 1 in 6, experience infertility. Giving people access to affordable fertility treatment can improve many people’s ability to start a family.
But even with this access, we still need incredible medical professionals who have the training to educate couples and treat infertility issues at their source. If you choose one of the career paths in this article, you could be one of those professionals who help others with infertility.
10 Different Careers in Fertility Medicine
Going into medicine is a noble pursuit, and if you want to focus on fertility medicine, you have plenty of options. Here are 10 different careers in fertility medicine you should explore.
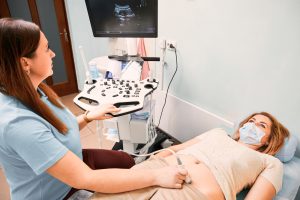
Sonographer
A sonographer is a medical professional who uses ultrasonic imaging equipment to diagnose various ailments. Getting an ultrasound during pregnancy is common, as it helps parents determine the age and health of the fetus. Ultrasounds can also be used for fertility issues.
After explaining the process to the patient, sonographers will capture clear ultrasounds of a patient’s uterus, ovaries, and endometrial lining to help physicians diagnose potential problems.
Lab Technician
A lab technician is responsible for performing technical, mechanical, and diagnostic tests in a laboratory. A lab technician who works for a fertility clinic or is trained to address fertility issues will use their knowledge to run the lab tests needed for a couple or an individual who is experiencing infertility.
Lab technicians may test samples for the presence or absence of hormones that help with family planning. They’ll also help with ordering supplies and managing equipment.
Medical Assistant
A medical assistant does a wide range of tasks, including showing patients to exam rooms, checking their height and weight, and taking them to the exam room. They would do the exact same thing in a fertility clinic, including sterilizing equipment with an autoclave.
A very experienced medical assistant will assist with on-site lab work (but is unlikely to take blood) and explain various fertility treatments or solutions to couples and individuals. They may administer the medications or explain the proper way to take them.
Patient Coordinator
A patient coordinator manages administrative tasks to ensure their patients receive comprehensive care. They’re often responsible for educating patients on registration, finances, and insurance companies. Some coordinators may speak to families about their fertility.
For example, they may suggest that patients work with a fertility app like Flo to track their menstrual and ovulation cycle.
Registered Nurse
A registered nurse (RN) is a medical professional who provides hands-on care in different medical and community settings. An RN in a fertility clinic could be responsible for administering in-vitro fertilization treatment and teaching patients how to self-administer treatment.
A fertility clinic RN will educate patients about their options before they make a decision. Nurses with a research focus or background, can help researchers come up with new reproductive technologies. A nurse can also pursue various certifications to expand their knowledge.
Embryologist
An embryologist works with patients, often indirectly, with fertility. They do this by helping with the different stages of IVF, from retrieval to the egg development and womb transfer. While they aren’t a doctor, their skills allow them to work with delicate cells like sperm cells and eggs.
Embryologists are also responsible for storing these cells for later use and relaying available treatment options to a patient’s doctor if they aren’t able to do this task themselves.
Midwife
A midwife can offer prenatal support to expectant patients. Some midwives are able to provide routine reproductive care, like Pap tests, but they often have to work alongside obstetricians and gynecologists. Many mothers choose a midwife to have a non-medicated/natural birth.
In regards to fertility specifically, midwives will provide psychological support and order medical tests to help parents through family planning. They may create comprehensive fertility plans.
Gynecologist
A gynecologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating conditions of the female reproductive system. They administer multiple services and tests, including pelvic exams and pap tests. They’ll also consult patients on menstruation issues, diagnose reproductive diseases, and help with family planning.
If a patient sees a gynecologist for fertility issues, they will conduct fertility monitoring. They’ll also consider how other health problems may impact fertility and create treatment plans.
Fertility Specialist
Fertility specialists are trained medical doctors who specialize in infertility-related conditions for both men and women. They’ll educate patients on fertility preservation, infertility treatments, and genetic diseases. Some further specialize in conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (POS).
A fertility specialist can administer a wide variety of treatments, including ovulation induction therapy, intrauterine insemination, in-vitro fertilization, and testicular sperm extraction (TESE).
Urologist
A urologist specializes in treating diseases of the urinary system for both men and women. Since the reproductive systems of males and females are closely linked to the urinary system, a urologist may be needed to diagnose and treat various fertility and reproductive issues.
In some cases, a urologist will conduct analysis on reproductive cells, perform imaging tests, or recommend genetic testing. They often work closely with other reproductive specialists.
In Conclusion…
Fertility issues are difficult to work through on your own. If you pursue one of the career paths listed in this article, you could do a lot to help those experiencing infertility. Many of these careers don’t even require medical school, so you can more easily switch to these roles quickly.
Author Bio: Veronica Turner is a health and lifestyle writer with over 10 years of experience. She creates compelling content on nutrition, fitness, mental health, and overall wellness.
Please also review AIHCP’s Case Management Certificate program and see if it meets your academic and professional goals. These programs are online and independent study and open to qualified professionals seeking a four year certification.

 Written By Lucy Peters
Written By Lucy Peters